creating-optimized-experience
DOCUMENTATION MOVED
Go to the new version of this page at https://docs.gmetri.com/guidelines-compatibility/guidelines/experience-optimizations
Creating Experiences Optimized for the Web
Tips and tricks to create an experience that runs smoothly on any device
Things to think about when building for the Web
Network Usage
Dependent on asset size. A 26Kb is better than a 100Kb image.
- Try keeping asset file size small. Use as much compression as possible to reduce the image size, as long as the quality doesn’t get affected.
Memory Usage
Affected by image resolution: pixels used by an image, calculated by (x*y)
- Don't use image/videos of a resolution higher than needed. A 50px 50px image is better than a 100px 100px image
- What this means is that even a 10Kb image of resolution 100,000px * 100,000px can crash your device, as it would take roughly 10GB of grahic memory.
- File size affects loading speed (more network usage for larger files). File resolution affects graphic memory (more memory for more pixels).
CPU/GPU Usage
Devices have a limited amount of processing capability. Videos consume a lot more CPU/GPU than images, 3D models.
- Bigger the video/3D model, more is the CPU and Memory consumption.
- Prefer images to videos: Try offloading as many effects as possible to images, instead of videos. Running too many (> 3) parallel videos in the same scene may not be supported by a lot of devices. You can use animations provided with images/pano images to try to produce a similar effect
Hardware Capability Limitation
All devices have inherent limitation on the number of audio/video streams they can run in parallel.
Video (number of parallel streams)
| Platform | No of HD videos (1280x720) | No of ~4K Videos (3840x1920) |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop/Laptop | 4 | 1 |
| Androids Phones | 4 | 1 |
| iOS Phones | 4 | 1 |
Audio (number of parallel streams)
| Platform | No of parallel audio streams |
|---|---|
| Desktop/Laptop | 7 |
| Androids Phones | 7 |
| iOS Phones | 7 |
Videos: Tips
Keep vides hidden until needed the scene
A non-hidden video get decoded by CPU/GPU and blocks its bandwidth. Hidden videos don't consume any CPU/GPU. So keep them hidden until needed, and hide them again if not needed anymore.
Images: Tips
- Transparent pixels use the same amount of memory as non-transparent ones
- Don’t use more pixels than being used in the viewport (the user’s monitor). Eg: If you use an Image that’s 5meters 5meters in 3D, and but placed 20 meters from the camera, its actual usage on the viewport is going to be only 100px 100px. In that case, use a 100px * 100px as the base image
Transparent pixels use the same amount of memory as non-transparent ones
Avoid using transparency for image placement.
Bad Example:
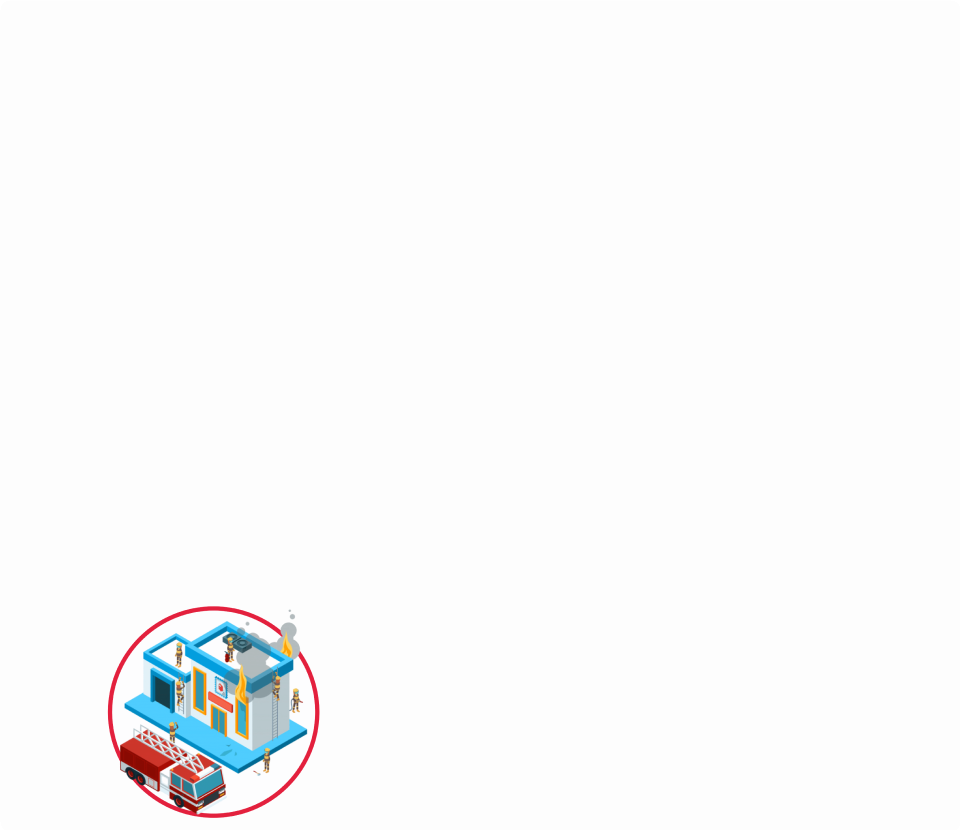
Dimensions: 960px x 831px. So it uses 797760 bytes = 0.79 MB in memory
Good Example
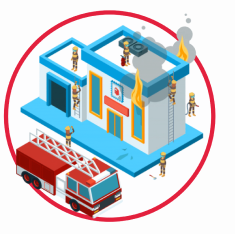
Dimensions: 235px x 235px. So it uses 55225 bytes = 0.05 MB in memory. 16x better than the bad example
Avoid decorational transparent images
Bad Example
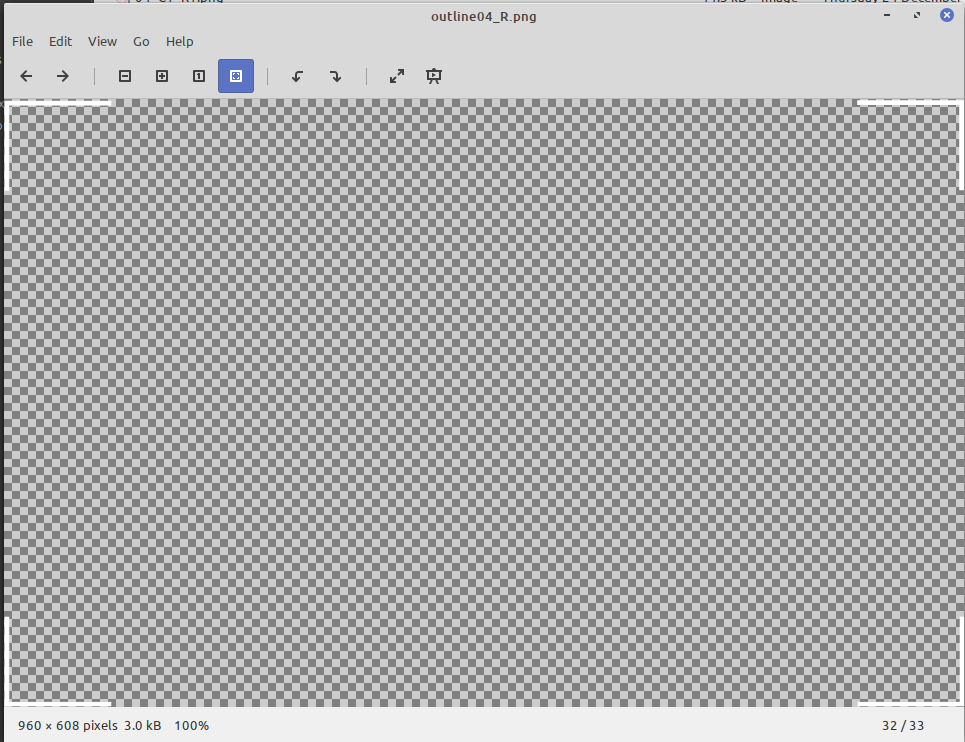 Although it's only 3Kb in size, its resolution is 960px * 608px, and so ends up using 0.5MB RAM!
Although it's only 3Kb in size, its resolution is 960px * 608px, and so ends up using 0.5MB RAM!
Use only minimum possible resolution of the image that’s being used in the viewport
Bad Example

Dimensions: 820px * 189px. i.e. it uses 154980 bytes (0.15MB) in memory
Good Example
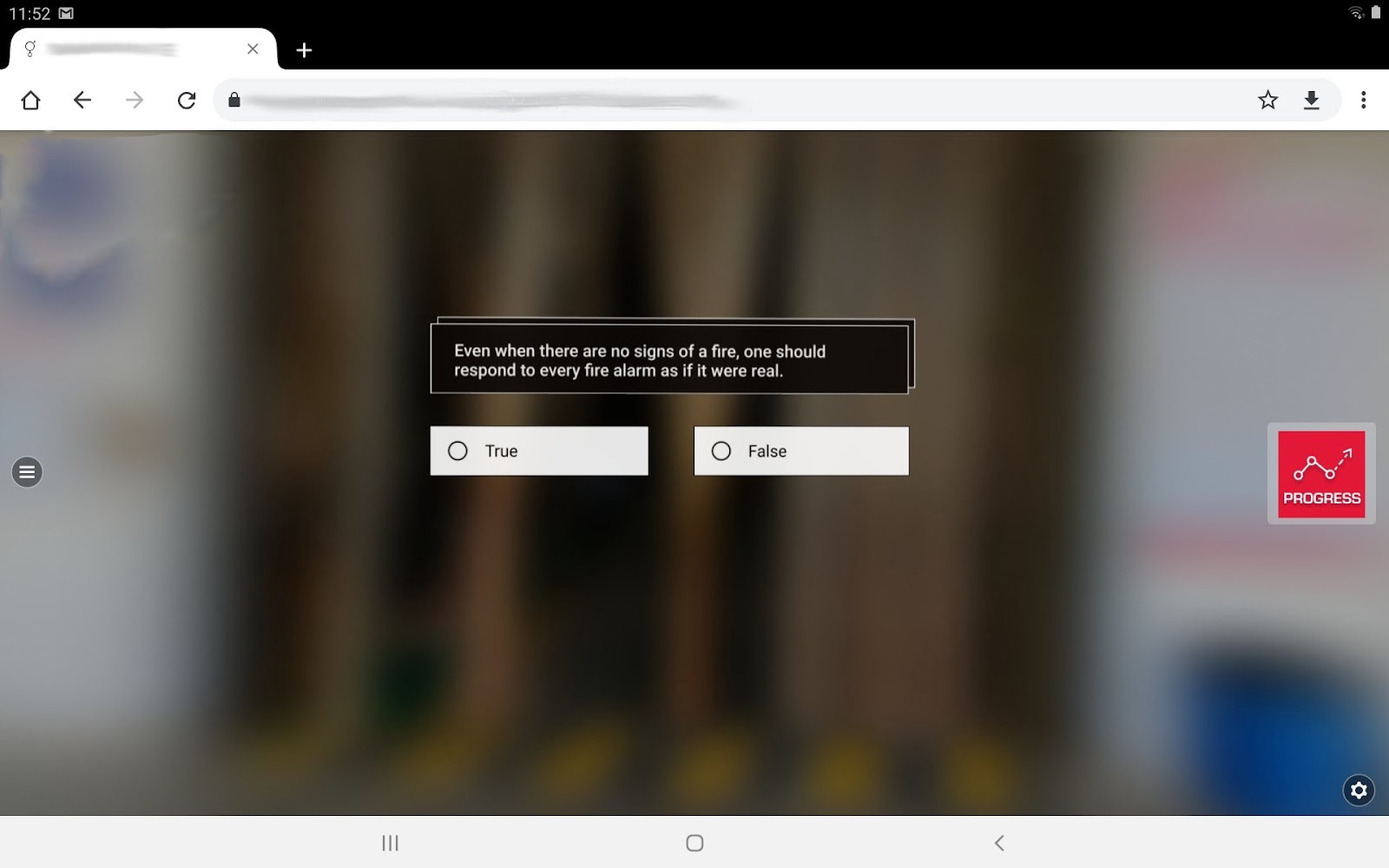
As you can see from the usage, the actual usage takes only about 300px 75px. So instead of using a 820px 189px image for it, use a 300px * 75px image. This would reduce the memory consumption by 7 times!